Advancing Healthcare Through Effective Clinical Data Management Practices
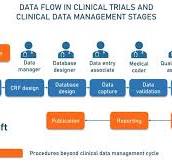
The Importance of Clinical Data Management
Clinical data management is a crucial aspect of healthcare and medical research that involves the collection, storage, analysis, and interpretation of data obtained during clinical trials and patient care. It plays a vital role in ensuring the accuracy, integrity, and confidentiality of medical information, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and advancements in medical science.
Ensuring Data Quality
One of the primary goals of clinical data management is to ensure the quality and reliability of data collected during clinical studies. By implementing rigorous data collection protocols and validation procedures, researchers can minimise errors and inconsistencies in the data, leading to more accurate results and conclusions.
Compliance with Regulations
In the healthcare industry, compliance with regulations such as Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines and data protection laws is essential to protect patient privacy and ensure the ethical conduct of clinical trials. Clinical data management practices help organisations adhere to these regulations by securely storing and managing sensitive patient information.
Facilitating Research and Analysis
Effective clinical data management facilitates research by providing researchers with access to high-quality data for analysis. By organising and standardising data in a centralised database, researchers can easily retrieve relevant information for study purposes, leading to more efficient research processes and meaningful insights.
Improving Patient Care
By accurately documenting patient information and treatment outcomes, clinical data management contributes to improving patient care. Healthcare providers can use this information to make informed decisions about patient treatment plans, monitor patient progress over time, and identify trends that may inform future healthcare practices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, clinical data management is a critical component of modern healthcare that ensures the accuracy, integrity, and security of medical information. By adhering to best practices in data collection, storage, and analysis, healthcare organisations can drive advancements in medical research, improve patient outcomes, and ultimately enhance the quality of care provided to patients.
Five Key Benefits of Clinical Data Management: Ensuring Accuracy, Compliance, Efficiency, Patient Care, and Scientific Advancement
- Ensures data accuracy and reliability in clinical studies
- Facilitates compliance with regulatory guidelines and data protection laws
- Enhances research efficiency by providing easy access to organised data
- Improves patient care through informed decision-making based on comprehensive patient information
- Contributes to advancements in medical science by enabling meaningful data analysis and interpretation
Challenges in Clinical Data Management: Addressing Cost, Complexity, and Security Concerns
- Complexity of data management processes can lead to errors and inconsistencies.
- High costs associated with implementing and maintaining clinical data management systems.
- Data security concerns due to the sensitive nature of patient information.
- Potential for breaches of confidentiality if data is not properly protected.
- Challenges in standardising data formats and terminology across different healthcare systems.
- Time-consuming manual data entry processes that can be prone to human error.
- Limited interoperability between different clinical data management systems, hindering data sharing and collaboration.
Ensures data accuracy and reliability in clinical studies
Ensuring data accuracy and reliability in clinical studies is a fundamental benefit of clinical data management. By implementing robust data collection protocols and validation procedures, clinical data management practices help minimise errors and inconsistencies in the data collected during research studies. This meticulous approach not only enhances the quality of research findings but also instils confidence in the integrity of the study outcomes. Researchers and healthcare professionals can rely on accurate and reliable data to make informed decisions, draw meaningful conclusions, and advance medical knowledge for the benefit of patients and society as a whole.
Facilitates compliance with regulatory guidelines and data protection laws
Facilitating compliance with regulatory guidelines and data protection laws is a significant benefit of clinical data management. By implementing robust data management practices, healthcare organisations can ensure that patient information is handled in accordance with strict regulations such as Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines and data protection laws. This not only safeguards patient privacy and confidentiality but also upholds the ethical standards required for conducting clinical trials and research. Effective data management helps in securely storing and managing sensitive patient data, thereby mitigating the risk of regulatory non-compliance and ensuring the integrity and security of healthcare information.
Enhances research efficiency by providing easy access to organised data
Clinical data management plays a crucial role in enhancing research efficiency by providing easy access to organised data. Researchers benefit greatly from the streamlined process of retrieving relevant information from centralised databases, allowing for quicker analysis and interpretation of data. This accessibility to well-organised data not only saves time but also enables researchers to focus on the core aspects of their studies, leading to more efficient research processes and ultimately contributing to the advancement of medical science and healthcare practices.
Improves patient care through informed decision-making based on comprehensive patient information
Clinical data management plays a vital role in improving patient care by enabling healthcare providers to make informed decisions based on comprehensive patient information. By accurately documenting and organising patient data, healthcare professionals have access to a wealth of information that can guide treatment plans, monitor progress, and identify trends in patient outcomes. This enables healthcare providers to deliver more personalised and effective care, ultimately leading to better health outcomes for patients.
Contributes to advancements in medical science by enabling meaningful data analysis and interpretation
Clinical data management plays a pivotal role in driving advancements in medical science by enabling meaningful data analysis and interpretation. Through systematic collection, organisation, and validation of clinical data, researchers can extract valuable insights that lead to the discovery of new treatments, identification of disease patterns, and improvement in healthcare practices. By leveraging well-managed clinical data, scientists can conduct robust analyses that contribute to the development of innovative medical solutions and enhance our understanding of complex health issues. This pro highlights how effective clinical data management is essential for pushing the boundaries of medical research and ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Complexity of data management processes can lead to errors and inconsistencies.
The complexity of data management processes within clinical data management can pose a significant challenge, potentially resulting in errors and inconsistencies. With the vast amount of data being collected, stored, and analysed during clinical trials and patient care, the risk of inaccuracies or discrepancies increases. The intricate nature of managing diverse data sources, ensuring data quality, and maintaining data integrity can overwhelm healthcare professionals and researchers, leading to inadvertent mistakes that could impact the reliability and validity of study findings. It is essential for organisations to implement robust quality control measures and training programmes to mitigate these risks and uphold the accuracy of clinical data for informed decision-making in healthcare.
High costs associated with implementing and maintaining clinical data management systems.
The high costs associated with implementing and maintaining clinical data management systems pose a significant challenge for healthcare organisations and research institutions. From the initial investment in software and hardware to ongoing maintenance, training, and support, the financial burden of establishing robust data management systems can be prohibitive. These costs may limit smaller healthcare providers or research facilities from adopting advanced data management technologies, potentially hindering their ability to efficiently collect, analyse, and utilise clinical data for improved patient care and research outcomes. As a result, finding cost-effective solutions while ensuring data quality and compliance remains a complex balancing act in the realm of clinical data management.
Data security concerns due to the sensitive nature of patient information.
One significant con of clinical data management is the heightened data security concerns arising from the sensitive nature of patient information. The storage and handling of vast amounts of personal health data pose a risk of unauthorised access, breaches, or misuse, potentially compromising patient privacy and confidentiality. Ensuring robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular audits, is essential to mitigate these risks. Failure to adequately address data security concerns can not only harm patients’ trust in healthcare providers but also lead to legal and ethical implications for organisations handling clinical data.
Potential for breaches of confidentiality if data is not properly protected.
The potential for breaches of confidentiality poses a significant con of clinical data management when data is not adequately protected. Inadequate security measures can leave sensitive patient information vulnerable to unauthorised access, leading to privacy violations and compromising the trust between healthcare providers and patients. Data breaches not only have legal implications but also ethical considerations, as they can result in serious consequences for individuals whose personal health information is exposed. Therefore, ensuring robust data protection protocols and encryption methods is essential to mitigate the risk of confidentiality breaches in clinical data management processes.
Challenges in standardising data formats and terminology across different healthcare systems.
One significant challenge in clinical data management is the difficulty of standardising data formats and terminology across diverse healthcare systems. The lack of uniformity in how data is structured and labelled hinders effective data exchange and interoperability between different healthcare providers and systems. This inconsistency can lead to errors in data interpretation, duplication of efforts, and delays in accessing critical information. Without a standardised approach to data formats and terminology, healthcare professionals may struggle to make informed decisions based on incomplete or inaccurate information, ultimately impacting patient care and clinical research outcomes. Efforts to address this challenge through the development of common data standards and interoperability protocols are essential to improving the efficiency and effectiveness of clinical data management practices.
Time-consuming manual data entry processes that can be prone to human error.
One significant drawback of clinical data management is the time-consuming nature of manual data entry processes, which are susceptible to human error. The reliance on manual input increases the likelihood of inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and data entry mistakes that can compromise the integrity and reliability of the collected data. This inefficiency not only hampers the speed and efficiency of data processing but also poses a risk to the validity of research findings and patient care outcomes. The need for meticulous verification and validation procedures to rectify errors further adds to the burden on healthcare professionals, highlighting the urgent need for more streamlined and automated data management solutions in clinical settings.
Limited interoperability between different clinical data management systems, hindering data sharing and collaboration.
Limited interoperability between different clinical data management systems poses a significant challenge in the healthcare industry, hindering seamless data sharing and collaboration among healthcare providers and researchers. The lack of compatibility between various systems makes it difficult to transfer and integrate data efficiently, leading to fragmented information silos that impede the exchange of critical patient information. This limitation not only hampers collaborative efforts in medical research but also compromises the continuity of care for patients, potentially impacting treatment outcomes and decision-making processes. Addressing this conundrum is essential to fostering a more interconnected healthcare ecosystem that promotes data sharing, innovation, and ultimately improves patient care.
