Exploring the Impact: Secondary Research in Academic and Business Environments
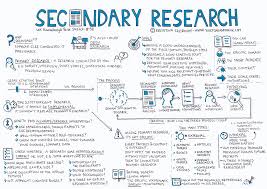
The Importance of Secondary Research in Academic and Business Settings
Secondary research, also known as desk research, plays a crucial role in both academic and business environments. It involves the collection and analysis of existing data and information that has already been published or gathered by others. While primary research involves collecting new data through experiments, surveys, or interviews, secondary research focuses on synthesising existing knowledge to gain insights and inform decision-making.
Benefits of Secondary Research
There are several benefits to conducting secondary research:
- Cost-Effective: Secondary research is often more cost-effective than primary research as it utilises existing data sources.
- Time-Saving: It saves time compared to conducting new studies or experiments.
- Breadth of Information: Secondary research allows researchers to access a wide range of information from various sources.
- Validation: It can help validate findings from primary research or provide additional context.
- Trend Analysis: By analysing historical data, trends and patterns can be identified to make informed decisions.
Applications of Secondary Research
In academia, secondary research is used to review existing literature, analyse previous studies, and build upon existing knowledge in a particular field. Researchers rely on secondary sources such as academic journals, books, reports, and online databases to support their arguments and contribute to the scholarly discourse.
In the business world, secondary research is essential for market analysis, competitor intelligence, industry trends assessment, and strategic decision-making. Companies use secondary data to understand consumer behaviour, market dynamics, regulatory environment, and other factors that impact their operations.
Challenges of Secondary Research
While secondary research offers numerous advantages, it also presents some challenges:
- Data Quality: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of secondary data sources can be a challenge.
- Data Availability: Accessing relevant data that meets specific research needs may be limited or require subscription fees.
- Bias: Existing data may be influenced by the perspectives or agendas of the original researchers or organisations.
- Data Interpretation: Interpreting secondary data requires critical thinking skills to avoid misinterpretation or drawing incorrect conclusions.
In Conclusion
Secondary research is a valuable tool for academics and businesses alike. By leveraging existing knowledge and information resources, researchers can gain valuable insights, validate findings, identify trends, and make informed decisions. While challenges exist in terms of data quality and interpretation, the benefits of secondary research far outweigh the drawbacks when conducted with care and diligence.
Understanding Secondary Research: Key Questions and Answers
- What is the difference between primary and secondary research?
- What is secondary research and examples?
- What is secondary research and why is it important?
- What are 3 methods of secondary research?
- What is secondary source of research?
- What is secondary research examples?
- What is primary & secondary research?
- What is meant by secondary data research?
What is the difference between primary and secondary research?
The key distinction between primary and secondary research lies in the methods of data collection. Primary research involves gathering new data directly from original sources through experiments, surveys, interviews, or observations. In contrast, secondary research involves analysing existing data that has already been collected and published by others. While primary research is tailored to address specific research questions and may offer unique insights, secondary research synthesises existing knowledge to provide context, validate findings, and identify trends. Both forms of research play important roles in academia and business settings, with primary research focusing on generating new data and secondary research on utilising existing information to enhance understanding and decision-making processes.
What is secondary research and examples?
Secondary research refers to the process of gathering and analysing existing data and information that has been previously collected by others. This type of research involves synthesising data from various sources such as academic journals, reports, books, and online databases to gain insights and inform decision-making. Examples of secondary research include literature reviews, market analysis reports, historical data analysis, and surveys conducted by other researchers or organisations. By utilising secondary research, individuals and businesses can access a wealth of knowledge to support their arguments, validate findings, identify trends, and make informed decisions based on existing information.
What is secondary research and why is it important?
Secondary research refers to the process of gathering and analysing existing data and information that has already been published or collected by others. It plays a critical role in academic and business settings by providing valuable insights, supporting decision-making processes, and validating findings from primary research. Secondary research is important because it offers a cost-effective and time-saving way to access a wide range of information sources, including academic journals, reports, books, and online databases. By leveraging existing knowledge and data, researchers can identify trends, validate hypotheses, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in their respective fields.
What are 3 methods of secondary research?
In the realm of secondary research, there are three primary methods commonly utilised to gather and analyse existing data and information. The first method is literature reviews, where researchers examine and synthesise relevant academic articles, books, and other published sources to gain insights into a specific topic or research question. The second method involves analysing existing datasets, which may include government reports, industry statistics, or historical records to extract valuable information for further analysis. Lastly, content analysis is another method used in secondary research, where researchers systematically evaluate and interpret various forms of media content such as documents, videos, or social media posts to uncover patterns or trends within the data. These methods play a vital role in expanding knowledge and informing decision-making processes across academic and business settings.
What is secondary source of research?
A secondary source of research refers to existing data and information that has been collected, analysed, and published by others for purposes other than the current study or investigation. Secondary sources can include academic journals, books, reports, government publications, and online databases that provide a wealth of knowledge on a particular topic. Researchers often rely on secondary sources to review existing literature, validate findings, identify trends, and build upon the work of others in their field. By utilising secondary research sources, scholars and professionals can access a wide range of information to inform their studies and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in various disciplines.
What is secondary research examples?
Secondary research examples encompass a wide range of sources and methodologies that involve the collection and analysis of existing data for various purposes. Common examples of secondary research include reviewing academic journals, books, reports, and online databases to gather information on a specific topic. Market research reports, government publications, historical data, and statistical records are also valuable sources of secondary research. By examining these existing sources of information, researchers can gain insights, validate findings, identify trends, and make informed decisions in academic, business, or other settings.
What is primary & secondary research?
Primary research involves the collection of new data directly from original sources through methods such as surveys, experiments, interviews, or observations. On the other hand, secondary research involves the analysis and synthesis of existing data and information that has already been published or gathered by others. While primary research generates firsthand data tailored to specific research objectives, secondary research utilises existing sources to provide context, validate findings, identify trends, and inform decision-making. Both primary and secondary research are valuable in academic and business settings, each serving distinct purposes in the research process.
What is meant by secondary data research?
Secondary data research refers to the process of collecting and analysing existing data and information that has been previously gathered by others for purposes other than the current research study. This type of research involves synthesising and interpreting data from sources such as academic journals, reports, surveys, databases, and other published materials to gain insights, validate findings, or support decision-making. Secondary data research allows researchers to leverage existing knowledge and resources to address research questions without the need to collect new data through primary methods like experiments or surveys. By utilising secondary data, researchers can explore trends, patterns, and relationships within a given context to enhance understanding and contribute to the body of knowledge in their field.
