Unveiling the Profound Effects of Environmental Factors on Health in the United Kingdom
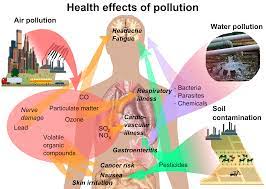
Title: The Impact of Environmental Factors on Health
Introduction:
Our health is influenced by various factors, including genetics, lifestyle choices, and access to healthcare. However, one crucial aspect that often goes unnoticed is the impact of our environment on our well-being. The built and natural environment in which we live, work, and play can significantly affect our physical and mental health. In this article, we will explore some of the key effects that environmental factors can have on our overall health.
Air Quality:
The quality of the air we breathe has a direct impact on our respiratory health. Poor air quality, often caused by pollution from vehicles, industry emissions, or indoor pollutants like tobacco smoke or mold, can lead to respiratory problems such as asthma and allergies. Long-term exposure to polluted air has also been linked to an increased risk of heart disease and lung cancer. It is essential for governments and individuals alike to take measures to improve air quality through stricter regulations and adopting cleaner technologies.
Green Spaces:
Access to green spaces such as parks, gardens, and forests has been shown to have numerous positive effects on our health. Spending time in nature has been associated with reduced stress levels, improved mood, increased physical activity levels, enhanced cognitive function, and a lower risk of chronic diseases like obesity and cardiovascular conditions. Incorporating green spaces into urban planning is vital for promoting community well-being and providing opportunities for relaxation and recreation.
Noise Pollution:
Excessive noise can have detrimental effects on our health. Living in noisy environments near busy roads or airports can disrupt sleep patterns leading to fatigue, irritability, decreased concentration levels, and impaired cognitive function. Prolonged exposure to high noise levels may also increase the risk of hypertension (high blood pressure), heart disease, and mental health issues such as anxiety or depression. Implementing effective noise reduction strategies in urban areas can help mitigate these adverse effects.
Water Quality:
Access to clean drinking water is crucial for maintaining good health. Contaminated water sources can transmit harmful bacteria, viruses, and parasites, leading to waterborne diseases such as cholera, dysentery, or gastrointestinal infections. Poor water quality not only affects physical health but also impacts sanitation and hygiene practices, further exacerbating the risk of diseases. Ensuring safe and clean water sources through proper infrastructure and regular monitoring is essential for safeguarding public health.
Built Environment:
Our built environment encompasses the design and layout of our cities, buildings, and transportation systems. A well-designed built environment can promote physical activity by providing walkable streets, bike lanes, and access to recreational facilities. On the other hand, urban sprawl, lack of green spaces, and limited access to healthy food options have been associated with sedentary lifestyles, obesity rates, and chronic diseases. Creating healthier built environments that prioritize active transportation options and incorporate sustainable design principles is crucial for fostering healthier communities.
Conclusion:
Understanding the effects of environmental factors on our health is paramount in promoting a healthier society. By prioritizing clean air, green spaces, reducing noise pollution, ensuring clean water sources and designing healthier built environments, we can create environments that support physical and mental well-being for all. Governments, urban planners, businesses, and individuals must collaborate to create sustainable communities that prioritize human health as a fundamental aspect of our shared future.
Common Questions About the Impact of Health on Well-being
- What are negative effects on human health?
- What are negative health effects examples?
- What are the factors that affect health?
- How does environment affect health?
What are negative effects on human health?
Negative effects on human health can arise from various sources and environmental factors. Here are some common negative effects:
- Air Pollution: Exposure to air pollution, whether from outdoor sources like vehicle emissions and industrial pollutants or indoor sources like tobacco smoke and household chemicals, can lead to respiratory issues such as asthma, allergies, bronchitis, and even lung cancer. Poor air quality also increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases and can exacerbate existing health conditions.
- Water Contamination: Consuming contaminated water can result in waterborne diseases such as cholera, dysentery, typhoid fever, and gastrointestinal infections. Contaminants like bacteria, viruses, parasites, heavy metals, and chemicals can have detrimental effects on human health and may cause acute or chronic illnesses.
- Noise Pollution: Prolonged exposure to excessive noise levels can lead to stress-related health problems including elevated blood pressure, heart disease, sleep disturbances, impaired cognitive function, hearing loss, and mental health issues such as anxiety and depression.
- Chemical Exposure: Exposure to hazardous chemicals in the environment or workplace can have severe health consequences. Chemicals found in pesticides, industrial waste products, cleaning agents, plastics (such as phthalates), and other sources may contribute to various health problems including cancer development, reproductive disorders, hormonal imbalances (endocrine disruption), neurological disorders, and respiratory issues.
- Lack of Green Spaces: Limited access to green spaces such as parks or natural environments in urban areas can negatively impact mental well-being. Lack of exposure to nature has been linked to increased stress levels, reduced cognitive function (including attention span), higher rates of mental illnesses like depression and anxiety disorders.
- Climate Change: The changing climate due to global warming has wide-ranging negative effects on human health. Heatwaves increase the risk of heat-related illnesses such as heatstroke; extreme weather events like hurricanes or floods pose physical dangers; changing precipitation patterns contribute to water scarcity and food insecurity; and the spread of infectious diseases may be influenced by changing climatic conditions.
- Built Environment: Poorly designed built environments with inadequate infrastructure, lack of walkability, limited access to healthy food options, and a prevalence of urban pollution can contribute to sedentary lifestyles, obesity rates, cardiovascular diseases, respiratory issues, and mental health problems.
It is crucial to address these negative effects on human health through effective policies, regulations, awareness campaigns, and sustainable practices to create healthier living environments for all.
What are negative health effects examples?
Negative health effects can arise from various environmental factors. Here are some examples:
- Air pollution: Long-term exposure to polluted air can lead to respiratory problems such as asthma, bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It can also increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and lung cancer.
- Water contamination: Drinking or coming into contact with contaminated water sources can cause waterborne diseases like cholera, dysentery, hepatitis A, and gastrointestinal infections.
- Noise pollution: Excessive noise levels can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to fatigue, irritability, reduced concentration, and impaired cognitive function. Prolonged exposure to high noise levels may also increase the risk of hypertension (high blood pressure), heart disease, and mental health issues.
- Chemical exposure: Exposure to harmful chemicals in the environment or workplace can have detrimental effects on health. For example, exposure to asbestos can cause lung diseases like asbestosis and mesothelioma. Pesticides and industrial chemicals may lead to various health issues including cancer, reproductive disorders, and neurological problems.
- Lack of green spaces: Limited access to green spaces like parks or gardens in urban areas can contribute to higher stress levels, reduced physical activity levels, increased obesity rates, and mental health issues such as anxiety and depression.
- Poor urban planning: Urban environments with inadequate infrastructure for active transportation (e.g., lack of sidewalks or bike lanes) may discourage physical activity and contribute to sedentary lifestyles, obesity rates, and related chronic conditions like diabetes or cardiovascular diseases.
- Indoor pollutants: Poor indoor air quality due to factors such as tobacco smoke, mold spores, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), or inadequate ventilation can cause respiratory problems like allergies or asthma exacerbations.
It is important to address these negative health effects through effective policies and interventions that prioritize clean air and water sources, reduce noise pollution, promote access to green spaces, and ensure safe and healthy built environments.
What are the factors that affect health?
There are numerous factors that can influence an individual’s health. These factors can be broadly categorized into two main types:
1. Internal Factors:
– Genetics: Our genetic makeup plays a significant role in determining our susceptibility to certain diseases and conditions.
– Age: Different age groups have varying health needs and vulnerabilities. Health concerns may change as we progress through different stages of life.
– Gender: Biological differences between males and females can lead to variations in health risks and outcomes.
– Pre-existing Conditions: Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions may have specific health considerations and requirements.
2. External Factors:
– Lifestyle Choices: Our daily habits, such as diet, physical activity, sleep patterns, substance use (e.g., tobacco, alcohol, drugs), and stress management, greatly impact our overall health.
– Socioeconomic Status: Income level, education, occupation, and access to resources like healthcare services, nutritious food, safe housing, and clean water can significantly influence health outcomes.
– Environment: The physical environment we live in has a substantial impact on our health. Factors such as air quality, water quality, noise levels, exposure to pollutants or toxins, access to green spaces or recreational facilities can affect our well-being.
– Social Support Networks: Having strong social connections and supportive relationships with family members, friends, or community networks can positively impact mental health and overall well-being.
– Healthcare Access: Availability of healthcare services including preventive care measures like vaccinations and screenings as well as timely access to medical treatments greatly affect individual health outcomes.
It is important to note that these factors are interconnected and often interact with each other. For instance, socioeconomic status can influence lifestyle choices and access to healthcare services. Understanding the various factors that affect health allows us to address them holistically for better overall well-being.
How does environment affect health?
The environment plays a significant role in shaping our health. Here are some ways in which the environment can affect our well-being:
- Air Quality: Poor air quality, often caused by pollution from vehicles, industrial emissions, or indoor pollutants, can lead to respiratory problems such as asthma and allergies. Long-term exposure to polluted air has also been linked to an increased risk of heart disease and lung cancer.
- Water Quality: Access to clean drinking water is crucial for maintaining good health. Contaminated water sources can transmit harmful bacteria, viruses, and parasites, leading to waterborne diseases such as cholera, dysentery, or gastrointestinal infections.
- Noise Pollution: Excessive noise can have detrimental effects on our health. Living in noisy environments near busy roads or airports can disrupt sleep patterns leading to fatigue, irritability, decreased concentration levels, and impaired cognitive function. Prolonged exposure to high noise levels may also increase the risk of hypertension (high blood pressure), heart disease, and mental health issues such as anxiety or depression.
- Green Spaces: Access to green spaces such as parks, gardens, and forests has been shown to have numerous positive effects on our health. Spending time in nature has been associated with reduced stress levels, improved mood, increased physical activity levels, enhanced cognitive function, and a lower risk of chronic diseases like obesity and cardiovascular conditions.
- Built Environment: The design and layout of our cities and buildings can impact our health. Well-designed built environments that prioritize active transportation options (walking or cycling), incorporate green spaces for recreation and relaxation, and provide access to healthy food options promote physical activity and healthier lifestyles.
- Climate Change: The changing climate patterns due to global warming have far-reaching consequences for human health. Rising temperatures increase the risk of heat-related illnesses while extreme weather events like hurricanes or floods can cause injuries and displacement. Climate change also affects the spread of infectious diseases like malaria or dengue fever.
It is important to recognize the impact of the environment on our health and take proactive measures to mitigate negative effects. Governments, policymakers, urban planners, businesses, and individuals all have a role to play in creating healthier environments that prioritize clean air, clean water, reduced noise pollution, access to green spaces, and sustainable design principles. By doing so, we can promote better health outcomes for individuals and communities alike.
