Navigating the Research Process: A Pathway to Discoveries and Insights
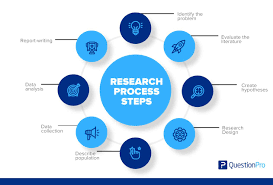
The Research Process: Unveiling the Path to Discoveries
Research is a fundamental process that drives progress and innovation across various fields. Whether it’s in science, social sciences, or humanities, the research process serves as a guiding light towards uncovering new knowledge and understanding. In this article, we will explore the essential steps involved in the research process and highlight its significance in advancing human understanding.
Identifying the Research Question:
Every research journey starts with a question. Researchers begin by identifying a specific problem or topic they wish to investigate. This initial step involves reviewing existing literature, brainstorming ideas, and narrowing down the focus to formulate a clear and concise research question. A well-defined question sets the stage for further exploration and provides direction throughout the research process.
Literature Review:
Before embarking on their own study, researchers delve into existing literature related to their chosen topic. This step helps them understand what has already been done in their field of interest, identify gaps in knowledge, and build upon previous findings. The literature review also aids researchers in developing hypotheses or conceptual frameworks that will guide their investigations.
Designing the Study:
Once the research question is established and relevant literature is reviewed, researchers proceed to design their study. This involves selecting appropriate methodologies, data collection techniques, and sampling strategies that align with their objectives. Careful consideration is given to ensure that ethical principles are upheld throughout the study design.
Data Collection:
With a well-designed plan in place, researchers begin collecting data relevant to their research question(s). This can involve conducting surveys or interviews, observing phenomena in natural settings, or analyzing pre-existing datasets. Rigorous data collection methods are employed to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Data Analysis:
After gathering all necessary data, researchers engage in thorough analysis using appropriate statistical or qualitative techniques depending on the nature of their study. This step involves organizing and interpreting data to draw meaningful conclusions from the findings. Statistical software or qualitative analysis tools are often employed to facilitate this process.
Drawing Conclusions:
Based on the analysis of the data, researchers draw conclusions that directly address their research question(s). This step involves critically evaluating the findings, considering their implications, and relating them back to existing theories or concepts. Researchers also discuss limitations and potential areas for further investigation.
Dissemination of Results:
The final step in the research process involves sharing the outcomes with the wider academic community and beyond. Researchers may choose to publish their findings in scientific journals, present at conferences, or communicate through various media platforms. Dissemination ensures that new knowledge is shared and contributes to the collective understanding within the field.
The research process is an iterative one, with each step informing and influencing subsequent stages. It requires patience, perseverance, and critical thinking skills to navigate through challenges and make significant contributions to knowledge. By following this systematic approach, researchers pave the way for innovation, problem-solving, and societal progress.
In conclusion, the research process serves as a roadmap for uncovering new insights and expanding our understanding of the world around us. From identifying a research question to disseminating results, each step plays a crucial role in advancing human knowledge. By embracing this process and encouraging interdisciplinary collaboration, we can continue pushing boundaries and making groundbreaking discoveries that shape our future.
Frequently Asked Questions: Research Process Guidance in the UK
- What is the process for conducting research?
- How do I get started with my research project?
- What resources are available to help me with my research?
- How can I ensure that my research is rigorous and of high quality?
- How do I identify an appropriate research methodology for my project?
- What ethical considerations should I take into account when conducting research?
What is the process for conducting research?
The process for conducting research typically involves the following steps:
- Identify the Research Topic: Begin by selecting a specific area or topic of interest that you wish to investigate. This could be based on personal curiosity, gaps in existing knowledge, or societal relevance.
- Conduct a Literature Review: Review existing literature and research related to your chosen topic. This step helps you understand what has already been done, identify gaps in knowledge, and build upon previous findings.
- Formulate Research Questions or Objectives: Based on your literature review, formulate clear and concise research questions or objectives that you aim to address through your study. These questions serve as a guide throughout the research process.
- Design the Study: Determine the appropriate research design and methodology for your study. Consider factors such as data collection methods (surveys, interviews, experiments), sampling techniques, and ethical considerations.
- Collect Data: Implement your chosen data collection methods to gather relevant information. This may involve conducting surveys, interviews, observations, or analyzing pre-existing datasets.
- Analyze Data: Once data is collected, analyze it using appropriate statistical or qualitative analysis techniques depending on the nature of your study. This step involves organizing and interpreting the data to draw meaningful conclusions.
- Draw Conclusions: Based on the analysis of your data, draw conclusions that directly address your research questions or objectives. Evaluate the significance and implications of your findings in relation to existing theories or concepts.
- Communicate Results: Share your research findings with others through various means such as publishing in academic journals, presenting at conferences, or communicating through media platforms. Disseminating results contributes to the collective knowledge within your field.
- Reflect and Revise: Reflect on your research process and outcomes critically. Consider limitations encountered during the study and potential areas for further investigation or improvement in future studies.
It is important to note that these steps are not always linear; researchers often revisit previous stages as they progress through the research process. Flexibility, adaptability, and attention to detail are key qualities for conducting successful research.
How do I get started with my research project?
Getting started with a research project can be an exciting but sometimes daunting task. Here are some steps to help you begin:
- Identify your research topic: Start by choosing a subject that interests you or aligns with your academic or professional goals. Consider current trends, gaps in knowledge, or areas that need further exploration.
- Conduct preliminary research: Before diving into your own study, conduct a literature review to familiarize yourself with existing research on the topic. This will help you understand the current state of knowledge and identify potential research questions or gaps to address.
- Refine your research question: Based on your preliminary research, narrow down and define a clear research question or objective. Make sure it is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Develop a research plan: Outline the key steps and methodologies you will use to answer your research question. Consider the type of data you need to collect, the methods of data collection (e.g., surveys, interviews, experiments), and any ethical considerations.
- Create a timeline: Break down your project into smaller tasks and assign realistic deadlines for each stage. This will help you stay organized and ensure that you make steady progress towards completing your research project.
- Gather necessary resources: Identify the resources needed for your study such as books, articles, datasets, equipment, or software tools. Access libraries, online databases, and academic journals to gather relevant information.
- Obtain necessary approvals: If applicable (e.g., for human subjects’ research), ensure that you obtain any required ethical approvals from relevant committees or institutions before proceeding with data collection.
- Collect and analyze data: Implement your chosen data collection methods and gather the necessary information for analysis. Use appropriate analytical techniques (quantitative or qualitative) to interpret the collected data effectively.
- Draw conclusions: Analyze the results of your study in light of your research question(s). Interpret the findings, identify patterns or trends, and draw meaningful conclusions. Discuss any limitations or areas for further research.
- Communicate your findings: Share your research outcomes through presentations, conferences, or by publishing in academic journals. Disseminate your work to contribute to the broader knowledge base within your field.
Remember that research projects often involve iterations and adjustments along the way. Be prepared to adapt your plan based on new insights or unexpected challenges that may arise during the process. Seek guidance from mentors, professors, or colleagues who can provide valuable feedback and support throughout your research journey.
What resources are available to help me with my research?
When embarking on a research journey, there are numerous resources available to assist you in your quest for knowledge. Here are some key resources that can support and enhance your research process:
- Libraries and Archives: Local libraries and archives offer a wealth of resources, including books, journals, newspapers, manuscripts, and historical documents. Librarians can provide guidance on locating relevant materials and navigating databases.
- Academic Databases: Online academic databases such as JSTOR, PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar provide access to a vast collection of scholarly articles, research papers, conference proceedings, and dissertations across various disciplines.
- Research Institutions: Universities and research institutions often have dedicated libraries or digital repositories that house research publications by their faculty members and researchers. These resources can be valuable for accessing cutting-edge studies in specific fields.
- Government Websites: Government websites at national or international levels offer access to official reports, statistical data, policy documents, and research findings related to various topics of interest.
- Professional Associations: Many professional associations have online platforms where they publish journals or provide access to member-exclusive resources. These associations often host conferences and workshops that facilitate networking with experts in your field.
- Online Research Communities: Platforms like ResearchGate or Academia.edu allow researchers to share their work and connect with others in their respective fields. These communities offer opportunities for collaboration, feedback on research ideas, and access to preprints or early-stage research findings.
- Open Access Journals: Open-access journals provide free access to peer-reviewed articles without subscription fees or paywalls. They promote the dissemination of knowledge worldwide by making scholarly work accessible to everyone.
- Online Forums and Discussion Boards: Participating in online forums or discussion boards related to your research topic can help you connect with fellow researchers who share similar interests or expertise. These platforms offer opportunities for exchanging ideas, seeking advice, or finding potential collaborators.
- Reference Management Software: Tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley assist in organizing and citing your research sources. These software applications streamline the process of managing references and generating bibliographies.
- Research Methodology Guides: Many books, online tutorials, and websites provide guidance on research methodologies, data analysis techniques, and research ethics. These resources offer valuable insights into conducting research effectively and rigorously.
Remember to critically evaluate the credibility and reliability of the resources you use for your research. Peer-reviewed journals, reputable institutions, and well-established databases are generally considered more reliable sources of information.
By utilizing these resources effectively, you can enhance the quality of your research, stay up-to-date with the latest developments in your field, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge.
How can I ensure that my research is rigorous and of high quality?
Ensuring rigorous and high-quality research is essential to produce reliable and credible results. Here are some key practices to consider:
- Clearly Define Research Objectives: Start by clearly defining your research objectives and research questions. This helps maintain focus and ensures that your study addresses a specific problem or gap in knowledge.
- Conduct a Thorough Literature Review: Before starting your research, conduct a comprehensive literature review to understand existing knowledge on the topic. This will help you build upon previous work, identify gaps, and ensure that your research adds value to the field.
- Use Appropriate Methodologies: Select appropriate methodologies that align with your research objectives. Whether quantitative, qualitative, or mixed methods, choose the most suitable approach to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Ensure Sample Representativeness: When selecting participants or samples for your study, strive for representativeness to ensure the findings can be generalized to the target population. Consider factors such as sample size, demographics, and inclusion criteria.
- Employ Rigorous Data Collection Techniques: Use reliable data collection techniques that are appropriate for your research design. Implement standardized protocols, ensure data accuracy, and minimize biases during data collection processes.
- Analyze Data Thoroughly: Apply robust statistical or qualitative analysis techniques to analyze your data accurately. Seek guidance from experts if needed and ensure transparency in reporting methods.
- Address Ethical Considerations: Adhere to ethical guidelines when conducting research involving human subjects or sensitive information. Obtain informed consent from participants, protect confidentiality, and consider potential risks and benefits associated with the study.
- Evaluate Validity and Reliability: Assess the validity (accuracy of measurement) and reliability (consistency of results) of your research instruments or measures used in data collection to ensure trustworthy findings.
- Engage in Peer Review: Seek feedback from peers or experts in your field through peer review processes before publishing your work. Incorporating constructive criticism strengthens the quality of your research and enhances its credibility.
- Maintain Transparency and Reproducibility: Clearly document your research process, including data collection procedures, analysis methods, and any limitations encountered. This transparency allows others to replicate or build upon your work, enhancing the overall quality of research in the field.
- Continuously Learn and Improve: Stay updated with advancements in your field through ongoing learning, attending conferences, and engaging in discussions with fellow researchers. Continuously improving your skills and knowledge will contribute to the quality of your research.
By following these practices, you can ensure that your research is rigorous, reliable, and contributes meaningfully to the existing body of knowledge. Remember that maintaining high-quality standards requires attention to detail, critical thinking, and a commitment to ethical conduct throughout the research process.
How do I identify an appropriate research methodology for my project?
Identifying an appropriate research methodology for your project is a crucial step that ensures the validity and reliability of your findings. Here are some key considerations to help you in this process:
- Research Objectives: Start by clearly defining the objectives of your study. Determine what you aim to achieve and what specific research questions you want to answer. This will guide you in selecting a methodology that aligns with your objectives.
- Nature of the Research Question: Consider the nature of your research question(s). Is it exploratory, descriptive, explanatory, or evaluative? Different types of research questions may require different methodologies. For example, if you want to explore a new topic or phenomenon, qualitative methods like interviews or focus groups may be more appropriate. On the other hand, if you aim to measure relationships or test hypotheses, quantitative methods such as surveys or experiments might be suitable.
- Data Availability: Assess the availability and accessibility of data relevant to your research question. If there is existing data that can address your objectives, secondary data analysis may be a viable option. However, if data is limited or unavailable, primary data collection methods will be necessary.
- Time and Resources: Consider the time frame and resources available for your project. Some methodologies require more time, funding, or specialized equipment than others. Evaluate whether you have access to these resources and whether they align with your project constraints.
- Ethical Considerations: Ensure that ethical principles are upheld throughout your research process. Consider any potential risks or ethical concerns associated with different methodologies and choose an approach that respects participants’ rights and confidentiality.
- Expertise and Skills: Assess your own expertise and skills as well as those available within your team or research community. Different methodologies require different technical knowledge and skills for data collection, analysis, and interpretation. Choose a methodology that aligns with the expertise available or consider collaborating with experts in the field.
- Literature Review: Conduct a thorough literature review to understand how previous studies have approached similar research questions. Identify which methodologies have been commonly used and critically evaluate their strengths and limitations. This will help you make an informed decision about the most suitable methodology for your project.
- Pilot Study: Consider conducting a pilot study or a small-scale version of your research to test the feasibility and effectiveness of different methodologies. This can help you identify any potential challenges or limitations before committing to a specific approach.
Remember, the choice of research methodology is not fixed and may evolve as your project progresses. It is important to remain flexible and open to adjustments if necessary. Consulting with experienced researchers or seeking guidance from your academic institution can also provide valuable insights in selecting an appropriate research methodology for your project.
What ethical considerations should I take into account when conducting research?
When conducting research, it is essential to consider and uphold ethical principles to ensure the protection and well-being of participants and the integrity of the study. Here are some key ethical considerations to keep in mind:
- Informed Consent: Obtain informed consent from all participants involved in the study. This means providing clear information about the purpose, procedures, risks, benefits, and voluntary nature of participation. Participants should have the freedom to ask questions and make an informed decision about their involvement.
- Privacy and Confidentiality: Safeguard the privacy and confidentiality of participants’ personal information. Collect data in a way that ensures anonymity or pseudonymity whenever possible. Store and handle data securely, ensuring that only authorized individuals have access.
- Minimize Harm: Take steps to minimize any potential physical, psychological, or emotional harm to participants. Assess potential risks associated with the research and implement appropriate measures to mitigate them.
- Respect for Autonomy: Respect participants’ autonomy by allowing them to withdraw from the study at any time without penalty or consequence. Ensure that they have control over their own data and can make decisions regarding its use.
- Research Design: Design studies that are scientifically valid, justifiable, and ethically sound. Ensure that research questions are relevant and contribute meaningfully to knowledge without causing unnecessary harm or discomfort.
- Conflict of Interest: Disclose any conflicts of interest that may arise during the research process. Be transparent about funding sources or any affiliations that could potentially influence the objectivity or outcomes of the study.
- Vulnerable Populations: Special care should be taken when involving vulnerable populations such as children, elderly individuals, prisoners, individuals with disabilities, or those with diminished decision-making capacity. Extra safeguards may be necessary to protect their rights and well-being.
- Research Ethics Review: Seek ethical approval from relevant institutional review boards (IRBs) or ethics committees before commencing your research project if required. These bodies evaluate research proposals to ensure compliance with ethical guidelines and standards.
- Data Handling and Reporting: Ensure accuracy and integrity in data collection, analysis, and reporting. Avoid selective reporting or misrepresentation of findings. Be transparent about any limitations or uncertainties associated with the study.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Respect cultural norms, values, and practices when conducting research involving diverse populations. Collaborate with local communities and stakeholders to ensure that the research is culturally appropriate and respectful.
These are general ethical considerations, but it is important to consult specific guidelines and regulations relevant to your field of study or research institution. By adhering to ethical principles, researchers can maintain the trust of participants, contribute responsibly to knowledge, and promote the well-being of individuals and communities involved in their studies.
