Unlocking the Potential of Stem Cells: A Journey Towards Medical Breakthroughs
The Fascinating World of Stem Cells
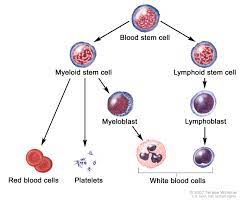
Stem cells are unique cells in the human body with the remarkable ability to develop into different cell types. They are the building blocks of life, playing a crucial role in the growth, repair, and regeneration of tissues and organs. Stem cells can be found in various parts of the body, including bone marrow, blood, and even embryos.
There are two main types of stem cells: embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells. Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent, meaning they can give rise to any type of cell in the body. They are derived from early-stage embryos and have the potential to treat a wide range of diseases and injuries.
On the other hand, adult stem cells are multipotent, which means they can only differentiate into certain types of cells depending on their origin. These stem cells play a vital role in maintaining and repairing specific tissues in the body throughout life.
The field of stem cell research holds great promise for medical advancements. Scientists are exploring ways to harness the potential of stem cells to develop new treatments for conditions such as spinal cord injuries, heart disease, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Stem cell therapy has already shown remarkable results in regenerating damaged tissues and organs in preclinical studies and clinical trials. This revolutionary approach offers hope for patients with debilitating conditions that currently have limited treatment options.
Despite the immense potential of stem cell research, ethical considerations surrounding the use of embryonic stem cells remain a topic of debate. Scientists continue to explore alternative sources of stem cells, such as induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which are generated from adult cells reprogrammed to behave like embryonic stem cells.
In conclusion, stem cells hold immense promise for revolutionizing healthcare by providing new avenues for treating a wide range of diseases and injuries. As research progresses and technology advances, we can expect further breakthroughs that will transform the way we approach medicine and improve patient outcomes.
Revolutionising Medicine: The Sixfold Promise of Stem Cell Research and Therapy
- Stem cells have the potential to repair and regenerate damaged tissues and organs.
- They offer new treatment options for a wide range of diseases and injuries.
- Stem cell therapy shows promise in treating conditions like spinal cord injuries, heart disease, and neurodegenerative disorders.
- Research on stem cells can lead to groundbreaking medical advancements and innovative therapies.
- Adult stem cells play a crucial role in maintaining tissue health throughout life.
- Stem cell research opens up possibilities for personalised medicine tailored to individual patients.
Six Key Challenges Facing Stem Cell Research and Therapy: Ethical Dilemmas, Health Risks, and Regulatory Hurdles
- Ethical concerns related to the use of embryonic stem cells
- Risk of tumour formation in stem cell therapy
- Potential for immune rejection in stem cell transplantation
- High cost associated with stem cell treatments
- Limited availability of approved stem cell therapies
- Complexity and challenges in regulating stem cell research and applications
Stem cells have the potential to repair and regenerate damaged tissues and organs.
Stem cells possess a remarkable ability to repair and regenerate damaged tissues and organs, offering a promising solution for treating a wide range of medical conditions. Through their unique capacity to differentiate into various cell types, stem cells can replace or repair injured cells, promoting tissue healing and regeneration. This pro of stem cells not only holds great potential for improving the quality of life for patients with degenerative diseases or injuries but also opens up new possibilities for innovative medical treatments that could revolutionize healthcare in the future.
They offer new treatment options for a wide range of diseases and injuries.
Stem cells offer a groundbreaking advantage in the field of medicine by providing new treatment options for a diverse array of diseases and injuries. Their unique ability to regenerate and repair damaged tissues and organs holds immense potential for revolutionizing healthcare. From spinal cord injuries to heart disease, diabetes to neurodegenerative disorders, stem cell therapy presents a promising avenue for addressing conditions that currently have limited treatment options. As research progresses and technology advances, the application of stem cells in medical treatments continues to expand, offering hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for patients worldwide.
Stem cell therapy shows promise in treating conditions like spinal cord injuries, heart disease, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Stem cell therapy offers a promising solution for treating a range of challenging conditions, including spinal cord injuries, heart disease, and neurodegenerative disorders. By harnessing the regenerative potential of stem cells, researchers are exploring innovative ways to repair damaged tissues and organs in these conditions. This groundbreaking approach holds great hope for patients suffering from debilitating injuries and diseases, offering the possibility of improved outcomes and quality of life through targeted and personalised treatments.
Research on stem cells can lead to groundbreaking medical advancements and innovative therapies.
Research on stem cells offers a promising avenue for groundbreaking medical advancements and innovative therapies. By unlocking the potential of stem cells to regenerate and repair damaged tissues and organs, scientists can develop revolutionary treatments for a wide range of diseases and injuries. From regenerating spinal cord tissue to repairing damaged heart muscle, the possibilities presented by stem cell research are truly transformative. With continued exploration and development in this field, we can anticipate the emergence of novel therapies that have the potential to improve patient outcomes and revolutionize healthcare practices.
Adult stem cells play a crucial role in maintaining tissue health throughout life.
Adult stem cells are essential components of the human body, playing a pivotal role in preserving tissue health and functionality over the course of a lifetime. These versatile cells have the remarkable ability to regenerate and repair specific tissues, ensuring the continuous maintenance and renewal of various organs. By replenishing damaged or aging cells, adult stem cells contribute significantly to the overall well-being and longevity of an individual. Their capacity to differentiate into specific cell types enables them to support tissue homeostasis and facilitate the healing process in response to injuries or degenerative conditions. The presence of adult stem cells underscores their importance in sustaining optimal tissue function and overall health throughout the lifespan.
Stem cell research opens up possibilities for personalised medicine tailored to individual patients.
Stem cell research offers a significant advantage in the realm of personalised medicine by paving the way for tailored treatments that cater to the unique needs of individual patients. By harnessing the regenerative and transformative capabilities of stem cells, scientists and healthcare professionals can develop customised therapies designed to address specific medical conditions based on a patient’s genetic makeup, disease progression, and overall health profile. This personalised approach not only enhances treatment efficacy but also minimises potential side effects, ultimately leading to more precise and effective healthcare interventions that can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Ethical concerns related to the use of embryonic stem cells
Ethical concerns surrounding the use of embryonic stem cells centre on the source of these cells, which involves the destruction of early-stage embryos. This raises complex moral questions about the beginning of life and the rights of the embryo. Critics argue that using embryonic stem cells for research or therapy disregards the sanctity of human life and may lead to ethical dilemmas regarding consent, commodification, and potential misuse of this technology. These concerns have sparked debates within scientific, religious, and political communities, highlighting the need for careful consideration and regulation in the field of stem cell research to navigate these ethical challenges responsibly.
Risk of tumour formation in stem cell therapy
One significant con associated with stem cell therapy is the risk of tumour formation. While stem cells have the potential to regenerate damaged tissues and organs, there is a concern that they may also uncontrollably divide and form tumours. This risk is particularly prominent with embryonic stem cells, which have a high capacity for proliferation. Tumour formation in stem cell therapy poses a serious challenge in the field of regenerative medicine, highlighting the importance of rigorous safety assessments and monitoring protocols to mitigate this potential adverse effect.
Potential for immune rejection in stem cell transplantation
One significant con of stem cell transplantation is the potential for immune rejection. When stem cells from a donor are transplanted into a recipient, there is a risk that the recipient’s immune system may recognize the transplanted cells as foreign and mount an immune response against them. This can lead to rejection of the transplanted stem cells, resulting in treatment failure and potential complications for the recipient. Strategies such as tissue matching and immunosuppressive drugs are often used to reduce the risk of immune rejection, but these approaches may not always be completely effective and can have their own set of side effects. The challenge of overcoming immune rejection remains a key hurdle in the field of stem cell transplantation, highlighting the need for further research and development to improve outcomes for patients undergoing such procedures.
High cost associated with stem cell treatments
One significant drawback of stem cell treatments is the high cost associated with them. The expenses involved in harvesting, processing, and administering stem cells can be prohibitive for many patients, making these innovative therapies financially out of reach for a large portion of the population. The high cost of stem cell treatments poses a barrier to access for individuals seeking potentially life-changing medical interventions, highlighting the need for greater affordability and accessibility in order to ensure that these promising therapies can benefit a wider range of patients in need.
Limited availability of approved stem cell therapies
One significant con of stem cell research and therapy is the limited availability of approved stem cell treatments. While the potential of stem cells to revolutionize medical treatments is vast, the process of developing and approving these therapies is complex and time-consuming. The regulatory landscape surrounding stem cell therapies is stringent, with strict criteria for safety, efficacy, and ethical considerations. As a result, there are currently a limited number of approved stem cell treatments available to patients, leading to challenges in accessing these innovative therapies for a wide range of conditions. This limitation underscores the need for continued research, clinical trials, and regulatory efforts to expand the availability of safe and effective stem cell treatments in the future.
Complexity and challenges in regulating stem cell research and applications
The complexity and challenges in regulating stem cell research and applications present a significant con in the field. With the diverse types of stem cells and their potential applications, establishing clear guidelines and ethical standards for their use becomes a daunting task. Issues such as patient safety, informed consent, intellectual property rights, and international collaboration further complicate the regulatory landscape. Additionally, the rapid pace of scientific advancements in stem cell technology requires regulatory bodies to constantly update policies to ensure responsible and ethical practices. Balancing innovation with oversight poses a continuous challenge in harnessing the full potential of stem cells while safeguarding against misuse or exploitation.
Latest articles
- Exploring the Foundations: Understanding Research Philosophy
- Exploring Different Types of Research: A Comprehensive Guide
- Unpacking Insights: A Guide to Qualitative Data Analysis in Research
- Embracing the Importance of Religious Education in Modern Society
- Exploring Thematic Analysis in Qualitative Research: Unveiling Patterns and Insights
Latest comments
Categories
- academic search
- academic search engines
- activate learning
- active learn
- adult
- alzheimer's
- alzheimer's research
- animal
- animal charity
- apple
- architecture
- bandlab
- bioinformatics
- building construction
- cancer
- cancer research
- cancer uk
- certificate programs
- child
- city
- community health
- construction
- consulting jobs
- content analysis
- department for education
- disruptive innovation
- distance learning centre
- drivers ed
- driving classes
- early childhood education
- early learning
- early years
- ece
- education
- education authority
- education city
- education jobs
- educational psychologist
- educational systems
- elementary
- elementary education
- elementary teacher
- engineering
- environment
- environmental health
- environmental science
- eu
- europe
- experimental research
- focus group
- food bank
- food pantry
- get into teaching
- google academic
- google research
- google scholar
- google search
- googled
- green construction
- health
- healthy life
- idea solutions
- iep
- indoor
- industrial
- industrial building
- innovate solutions
- innovation
- innovation software
- innovative management solution
- innovative software services
- interdisciplinary studies
- international marketing
- interpretative phenomenological analysis
- ipa
- journal of international
- journal of marketing
- journal of marketing research
- learning
- learningonline
- longitudinal research
- longitudinal study
- ma
- maed
- management
- management innovation
- marketing
- marketing research
- master of education
- masters
- math
- math teacher
- maths
- meeting
- memoir
- memoirs
- mental well being
- mental wellbeing
- method
- methods
- microsoft
- microsoft office
- ministry of education
- montessori
- mrc
- neom
- nih
- nursing
- observational research
- office 365
- online academy
- online learning academy
- online school
- onlinestudies
- participant observation
- pe teacher
- pharmaceutical
- philosophy
- physical education
- postgraduate
- postgraduate courses
- preschool teacher
- primary education
- product innovation
- psychology
- public health
- qualitative analysis
- qualitative data
- qualitative research journal
- reggio emilia
- religious education
- research
- research gates
- research scholar
- researchgate
- rspca
- scholar google
- scholare
- schools
- science
- search engines
- secondary
- secondary data
- secondary education
- sen teacher
- sociology
- special education
- special education teacher
- sped
- spiritual well being
- spiritual wellbeing
- student
- survey research
- synonym
- teach
- teacher
- teachers
- teaching
- ted talk
- tertiary education
- thematic analysis
- times higher
- train
- training
- ttra
- uk
- Uncategorized
- university
- university student
- university times
- urban design
- volunteer abroad
- week
- wellbe
